FullStory is a platform for analyzing user interactions, data recording and searching, and much more. FullStory's Digital Experience Intelligence (DXI) capability lets you measure and improve your users' overall digital experience.
RudderStack supports FullStory as a destination to which you can send your event data seamlessly.
Getting started
To send your events to FullStory via RudderStack, you will first need to add it as a destination in the RudderStack dashboard. Before you get started, check if the source platform supports sending events to FullStory by referring to the table below:
| Connection Mode | Web | Mobile | Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device mode | Supported | Supported | - |
| Cloud mode | - | - | - |
Once you have confirmed that the platform supports sending events to FullStory, perform the steps below:
- From your RudderStack dashboard, add the source. Then, select FullStory from the list of destinations.
- Assign a name to your destination and click on Next. You should be able to see the following screen:
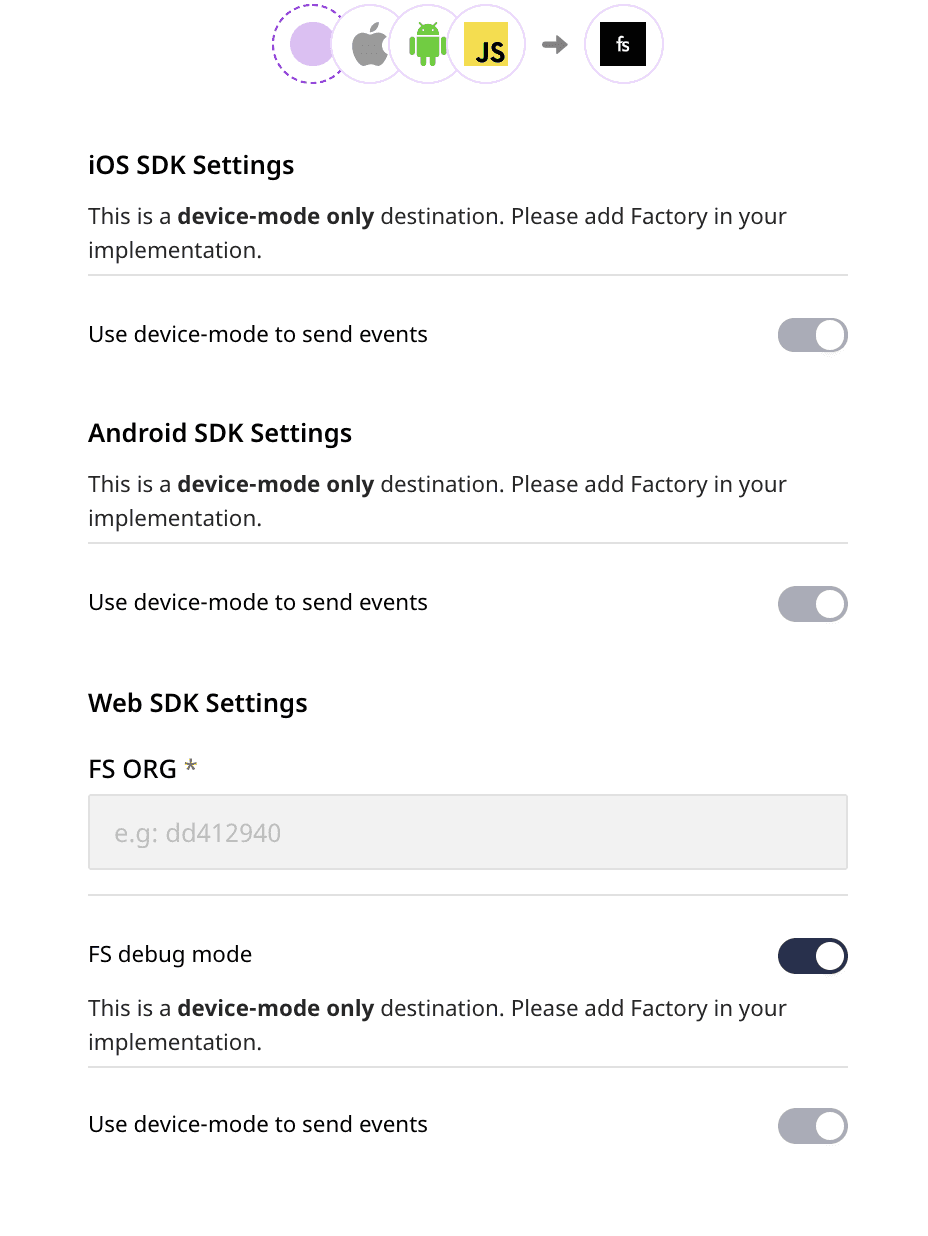
Connection settings
To configure the destination, you will need to enter the following settings:
- FS ORG: To get this value, log into your FullStory account and navigate to Settings - General. Then, copy the value present in the following line:
window['_fs_org'] = 'some_value';In the above snippet, some_value represents the value for the FS ORG field.
- To enable FullStory debugging, you can enable the FS debug mode option.
Adding device mode integration
To add FullStory to your project, follow the steps below depending on your platform of integration.
iOS
To add FullStory to your iOS project, follow these steps:
- In your
Podfile, add the following dependencies:
pod 'FullStory', :http => 'https://ios-releases.fullstory.com/fullstory-1.18.0-xcframework.tar.gz'pod 'Rudder-FullStory', :git => 'https://github.com/rudderlabs/rudder-integration-fullstory-ios.git', :tag => 'v1.0.0'- After adding the dependencies followed by a
pod installcommand, add the following imports to yourAppDelegate.mfile:
#import <Rudder/Rudder.h>#import <RudderFullStoryFactory.h>- Then, initialize your
RSClientas shown:
RSConfigBuilder *configBuilder = [[RSConfigBuilder alloc] init];[configBuilder withDataPlaneUrl:dataPlaneUrl];[configBuilder withFactory:[RudderFullStoryFactory instance]];RSClient *rudderClient = [RSClient getInstance:writeKey config:[configBuilder build]];To complete the FullStory integration, you need to specify which FullStory organization to record. Follow these steps:
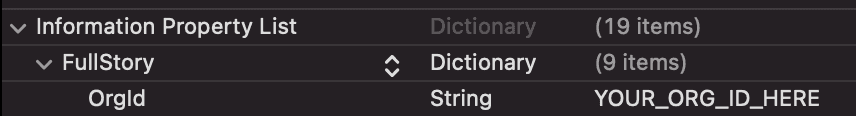
Open your app's
Info.plist.From the menu, choose Editor - Add Item. Set the key name to
FullStory, and the type toDictionary.Right-click on the FullStory row, and choose Add Row. Set the key name to
OrgId, and the type toString. For the value, paste your assigned organization ID.When configured correctly, the
Info.plistentry should look as follows:
Android
To add FullStory to your Android project, follow these steps:
- Open your
app/build.gradle(Module: app) file and add the following under thedependenciessection:
implementation 'com.rudderstack.android.sdk:core:1.0.22'implementation 'com.rudderstack.android.integration:fullstory:1.0.0'implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.6'// FullStoryrepositories { maven { url "https://maven.fullstory.com" }}implementation 'com.fullstory:instrumentation-full:1.18.0@aar'- Then, add the FullStory Maven plugin to your build script. To do so, add the following snippet into the
Gradle Scriptssection of your rootbuild.gradle:
buildscript { repositories { google() jcenter() maven { url "https://maven.fullstory.com" } } dependencies { classpath 'com.fullstory:gradle-plugin-local:PLUGIN_VERSION' // NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong // in the individual module build.gradle files }}
allprojects { repositories { google() mavenCentral() }}Make sure that you replace
PLUGIN_VERSIONwith the correct version of the FullStory Android plugin. You can find the latest release notes here (this is currently 1.18.0).To apply the FullStory plugin, add the following snippet into your app-specific
build.gradle(if your Gradle file adds plugins via plugin ID):
plugins { id 'com.android.application' id 'fullstory'}fullstory { org 'YOUR_ORG_ID_HERE'}- If your Gradle file applies plugins, use the following snippet instead:

YOUR_ORG_ID_HERE above with your organization ID.- To apply FullStory to all variants, including those used at debug time, add the following line below
org:
org 'YOUR_ORG_ID_HERE'enabledVariants 'all'- Add the following permissions, if not added already, to your
AndroidManifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>- Finally, initialize the RudderStack SDK in your
Applicationclass'onCreate()method as shown:
// initializing Rudder SDKval rudderClient = RudderClient.getInstance( this, WRITE_KEY, RudderConfig.Builder() .withDataPlaneUrl(DATA_PLANE_URL) .withFactory(FullStoryIntegrationFactory.FACTORY) .build() )Identify
The identify call is used to uniquely identify a user in FullStory.
A sample identify call looks like the following snippet:
rudderanalytics.identify("userId", { name: "John", email: "john@xyz.com",});The above call is translated to a FullStory identify call as follows:
userIdis sent as theuid.- The remaining traits are passed on as is.
In the web device mode, if the userId is not explicitly provided, then the anonymousId of the user is sent as the uid instead.
displayName and email
displayName and email are both optional traits that can passed on to FullStory and are treated specially. Once these traits are specified in the identify call, they will show up automatically the next time the user list is browsed in FullStory.
A sample identify call using the displayName and email is as shown:
rudderanalytics.identify("1234", { displayName: "John Falko", email: "john@xyz.com", country: "UK",});For more information on the displayName and email traits, refer to the FullStory documentation.
Track
A track call lets you track custom events as they occur in your web application.
A sample track call looks like the following snippet:
rudderanalytics.track("Order Completed", { orderId: "1234567", price: "567", currency: "USD",});A track call is directly passed on to FullStory via its FS.event method. All the associated event properties are also passed to FullStory via this call.
Page
A page call contains information such as the URL or the name of the web page visited by the user.
By default, all page calls are sent to FullStory as events. A sample page call looks like the following:
rudderanalytics.page("homepage");The above call sends an event to FullStory with a name Viewed a Page. It also sends the following properties with the event:
name*if provided (homepagein the sample example above)pathreferrersearchtitleurl
Any additional properties passed to the page call are also passed on to FullStory.
Screen
The screen method allows you to record whenever a user sees the mobile screen, along with any associated optional properties. This call is similar to the page call, but exclusive to your mobile device.
A sample screen call looks like the following code snippet:
MainApplication.rudderClient.screen("Sample Screen Name", RudderProperty() .putValue("prop_key","prop_value"));In the above snippet, RudderStack captures all the information related to the viewed screen, along with any additional info associated with that event. In FullStory, the above screen call will be shown as - Screen Viewed along with the properties.
Note that the screen call will be sent to FullStory as a custom event.
Reset
The reset method calls will release the identity of the current user and create a new anonymous session. It should be called when the users log out. For more information, refer to the FullStory Reset API.
A sample reset call for iOS is as shown:
[[RSClient sharedInstance] reset];For Android, a sample reset call is shown below:
MainApplication.rudderClient.reset()FAQs
How do I get the value for the field FS ORG?
To get the value for the FS ORG * field in the RudderStack Connection Settings, please follow these steps:
- Login to your FullStory dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings - General.
- Go to the following line and copy the value present there:
window['_fs_org'] = 'fullstory_org';
In this case, fullstory_org is your FS ORG value.
How do I prevent FullStory from automatically recording on startup?
By default, FullStory will automatically request a session and start recording on the app's startup. If you need to start recording the app only when certain conditions are met, then you can use the new RecordOnStart feature. Configuring FullStory to disable RecordOnStart will prevent any recording until you explicitly invoke FS.restart.
To prevent FullStory from recording on start, follow these steps:
In your iOS app’s Info.plist's FullStory dictionary, add a RecordOnStart key of type Boolean with a value of NO. Refer to the FullStory iOS documentation for more information.
In case of Android, go to your FullStory plugin configuration (where you set your organiation ID) and set the following:
fullstory {org 'YOUR_ORG_ID_HERE'recordOnStart false}Refer to the FullStory Android documentation for more information.
How do I subclass from an application in Android?
FullStory requires that you enable MultiDex. If your minSdkVersion is set to 21 or higher, Multidex is enabled by default. In this case, you will need to extend android.app.Application, otherwise there will be a build error. If your minSdkVersion is lower than 21, you will need to subclass from androidx.multidex.MultiDexApplication instead.
If you're using Java and if you do not have an application class, you will need to create one. In your App.java, add the following:
import android.app.Application;public class App extends Application {...}If you're using Kotlin and if you do not have an application class, you will need to create one, and add the following in your App.kt:
import android.app.Applicationclass App: Application() {...}Then, set android:name="App" in your AndroidManifest.xml under the <application> tag as shown:
<applicationandroid:name="App" ….I encountered this error: Build was configured to prefer settings repositories over project repositories but repository 'Google' was added by build file 'build.gradle'. What do I do?
Go to your settings.gradle file located in the root, and then comment or remove this line: repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS) as shown in the following snippet:
dependencyResolutionManagement { // repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS) repositories { google() mavenCentral() jcenter() // Warning: this repository is going to shut down soon }}rootProject.name = "FullStory_Sample_App"include ':app'For more information, refer to the FullStory documentation.
Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.